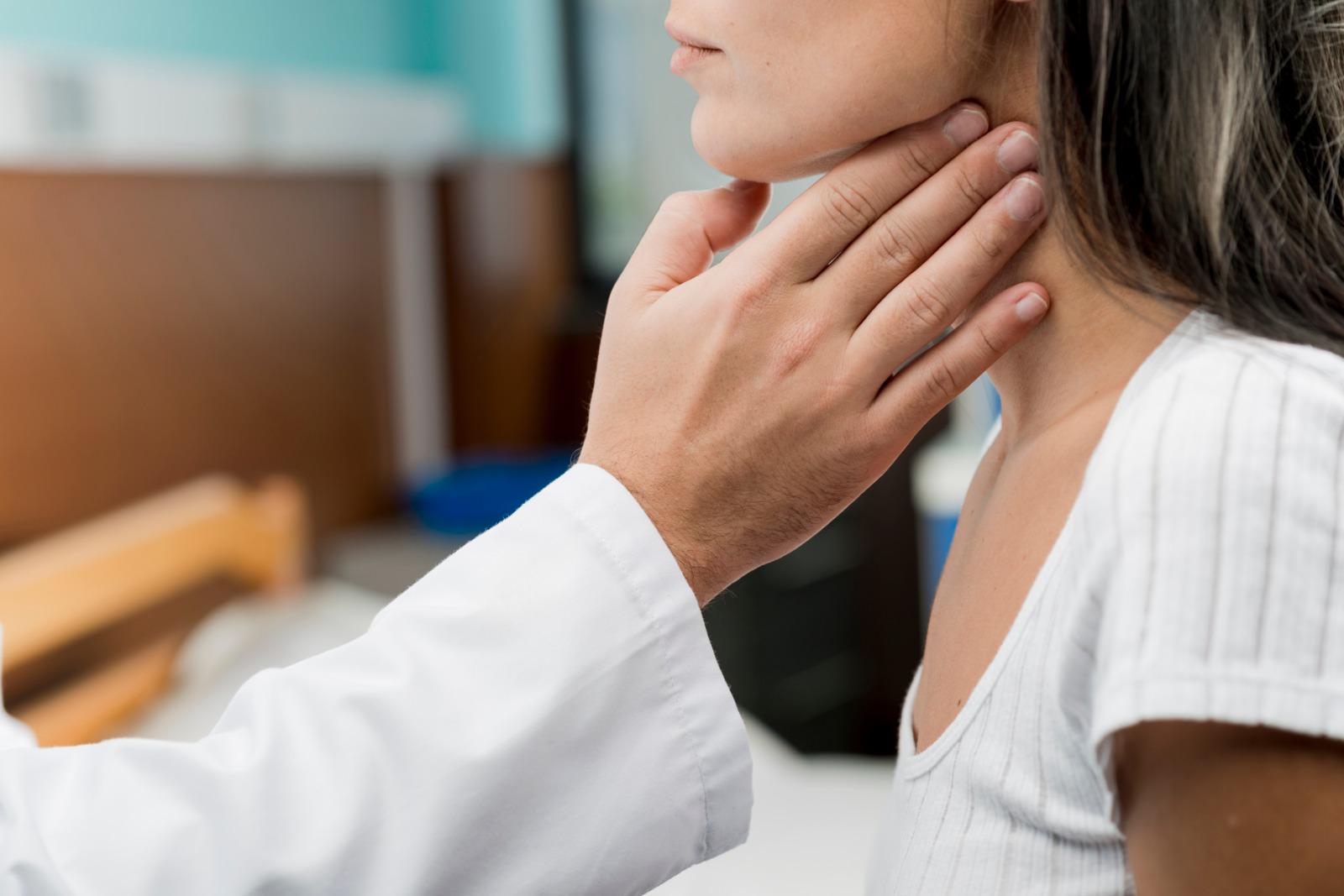
Thyroidectomy is a
surgical procedure for the treatment of malignant (malignant) and benign
(benign) changes in the thyroid gland, involving the removal of the entire
thyroid gland. Depending on the indication, thyroidectomy can be
performed as a total thyroidectomy (TT; complete removal of the thyroid gland)
or subtotal thyroidectomy (partial removal of the thyroid gland). In the case
of a unilateral thyroidectomy, i.e. the complete removal of one of the two lobes
of the thyroid gland, this is called a hemithyroidectomy (HT) or lobectomy of
the thyroid gland.
Indications
Multinodular goitre
Graves' disease
Papillary thyroid
carcinoma
Follicular thyroid
carcinoma
Medullary thyroid
carcinoma
Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma
Before surgery
- Preliminary examination
to determine the indication - after inspection and palpation of the thyroid
gland and sonographic imaging (thyroid ultrasound), hormone determinations and,
depending on the problem, fine needle biopsies (tissue samples) are taken for
further clarification.
- Pre-operative
examinations - the pre-operative examination is carried out for all indications
for thyroidectomy. It includes, among other things, a clinical physical
examination with measurement of heart rate and blood pressure. An X-ray chest
examination is also necessary. Furthermore, an ECG is written and a blood
sample is taken to determine various laboratory parameters such as kidney
parameters (urea, creatinine, creatinine clearance if necessary) and the INR
determination (blood clotting), and other laboratory parameters if necessary.
Further special examinations are carried out depending on the indication.
Preliminary examination
for indication
- after inspection and palpation of the
thyroid gland and sonographic imaging (thyroid ultrasound), hormone
determinations and, depending on the problem, fine-needle biopsies (tissue
samples) are taken for further clarification.
- Pre-operative
examinations - the pre-operative examination is carried out for all indications
for thyroidectomy. It includes, among other things, a clinical physical
examination with measurement of heart rate and blood pressure. An X-ray chest
examination is also necessary. Furthermore, an ECG is written and a blood
sample is taken to determine various laboratory parameters such as kidney
parameters (urea, creatinine, creatinine clearance if necessary) and the INR
determination (blood clotting), and other laboratory parameters if necessary.
Further special examinations are carried out depending on the indication.
The surgical procedure
First, the anterior
surface of the thyroid gland is exposed so that the isthmus (tissue bridge
between the two thyroid lobes) on the trachea can be cut and treated with
haemostatic grafting. The parts of the thyroid gland to be removed are then
detached from the surrounding area and the blood vessels supplying and draining
the gland are cut. Taking into account the position of the recurrent laryngeal
nerve (vocal cord nerve) and the parathyroid glands, the trachea (windpipe) is
approached, the connective tissue layer between the thyroid gland and the
windpipe is cut and the tissue removed.



.png)