01
2021
Mar
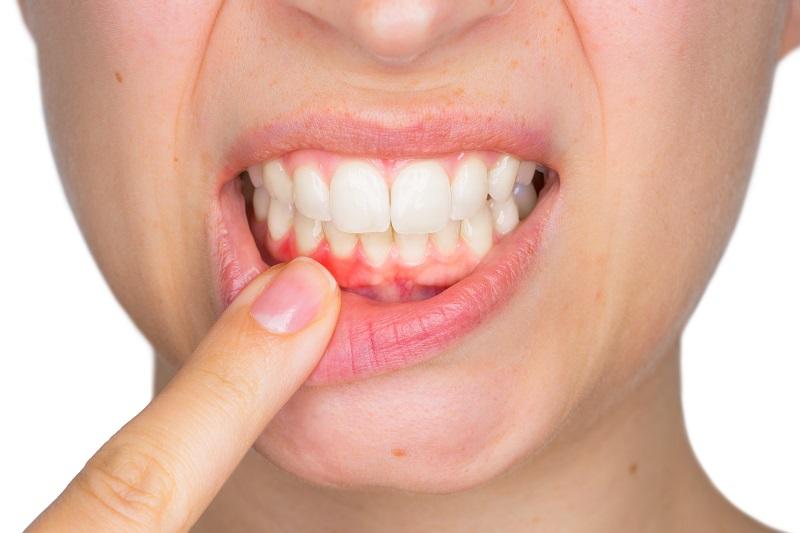
Gum disease (periodontal disease) is an infectious disease that affects the tissues surrounding and supporting the tooth, not the tooth. Even teeth that have no decay can be lost due to this disease. It is quite difficult to notice because it is usually painless.
Bacterial plaque:
The main cause of gum disease is bacterial plaque, which begins to form rapidly after eating. Bacterial plaque causes the formation of tartars in the progressive process, creating an obstacle between the gum and the tooth and leading to the following results:
• Easily bleeding gums
• Red, swollen, sensitive gums
•Constant bad breath or bad taste
• Loose or detached permanent teeth
• Any change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
• Any change in the alignment of partial dentures
Factors that increase the risk of developing gum disease:
• Missing or incorrect mouth care
• Use of cigarettes and tobacco products
• Genetic causes
• Cleaning problems caused by crooked teeth
• Pregnancy
• Diabetes
• Drugs including steroids, certain anti-epilepsy drugs, cancer treatment drugs, certain calcium channel blockers and oral contraceptives
The early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis, and early detection is an important factor that facilitates the treatment of this disease. Early detection at this stage accelerates the treatment proces. It can usually be eliminated by a professional cleaning followed by daily brushing and flossing.
Advanced gum disease is called periodontitis. It can cause tissue and bone loss that supports teeth and can become more severe over time. Otherwise, your teeth will loosenig and start moving in your mouth. This is the most common form of periodontitis in adults, but it can occur at any age. It usually worsens gradually, but there can be periods of rapid progress.
Aggressive periodontitis is a highly destructive form of periodontal disease that occurs in patients who are otherwise healthy. Common features include rapid tissue and bone loss and can occur in some parts of the mouth or the entire mouth.
Regular brushing and flossing, regular checkups by your dentist, and early diagnosis will prevent you from losing your tooth, and ensuring that this disease is eliminated without progress.



.png)